It may not be possible to prevent glaucoma, but it is easy to diagnose and is treatable. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that by age 40 adults with no symptoms or risk factors of glaucoma should have a complete baseline eye disease exam. A follow-up scheduled will be developed based on the findings. Those with increased risk of glaucoma should begin earlier.
A comprehensive eye examination includes:
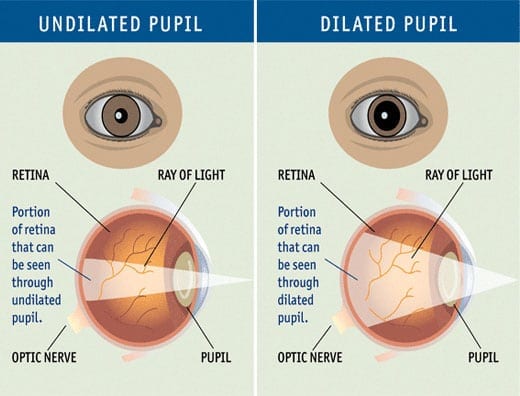
Dilation (shown Above)
Drops are placed in the eyes to dilate, or widen the pupils to look for signs of damage to the retina and optic nerve.
Tonometry
A test that measures eye pressure. Numbing drops may be applied. (See below)
Visual field test
Measures your side or peripheral vision. Loss of side vision is the first sign of glaucoma.
Visual acuity test
An eye chart measures how well you see at various distances. People can have good acuity, but still have glaucoma.

Photos courtesy of National Eye Institute